Surveying

Service
Surveying is the foundation of the Construction Division that measures the exact location of the land and creates spatial data. In recent years, the development of satellite positioning systems has made it possible to quickly collect and provide highly accurate data. We are making use of 3D measurement equipment, GNSS surveying equipment, and TS to improve efficiency from reference point surveying to site surveying. Further, we actively deploy, use, and apply information on technological advances and innovations in surveying instruments to meet the diverse demands of our clients and provide high-quality results.

- Main Business
Control point surveying
Control point surveying is a type of survey in which a new point is established based on a known point. Control point surveying is classified into grades 1 through 4, and each grade has different working methods, distances between known points, and distances between new points. Known control points include basic control points such as GPS-based control stations, triangulation stations, and bench marks. The results obtained from control point surveying are used as “standards and foundations” for mapping and various types of surveys.
Control point surveying

Topographical surveying
Topographical surveying refers to surveying for the preparation of topographic or planimetric maps. Topographic maps are faithful representations of land features and landforms on the ground, that is, the ups and downs of the land and other topographic characteristics and are generally classified into two categories: plane-table surveying and aerial photogrammetric surveying. Topographical surveying is an important process for creating topographic maps. The equipment used includes total station (TS) and GNSS surveying equipment, which improves accuracy and makes it possible to handle drawings numerically. In recent years, we have been using 3D measurement equipment (terrestrial 3D laser scanners, UAV laser scanners, MMS, etc.) to improve work efficiency.
Topographical surveying

Applied surveying
Applied surveying is a field of surveying that uses basic and public surveying techniques to public works projects.
Specifically, it refers to surveying used for planning and land acquisition for roads, rivers, parks, etc.
Applied surveying is divided into three main areas:
・Route surveying
・River surveying
・Site surveying
Route surveying
Route surveying refers to surveying (alignment determination, centerline surveying, temporary BM installation surveying, longitudinal surveying, cross-sectional surveying, and site width stakeout surveying) used for research, planning, and design to create road, railroad, and other linear structures.
Route surveying
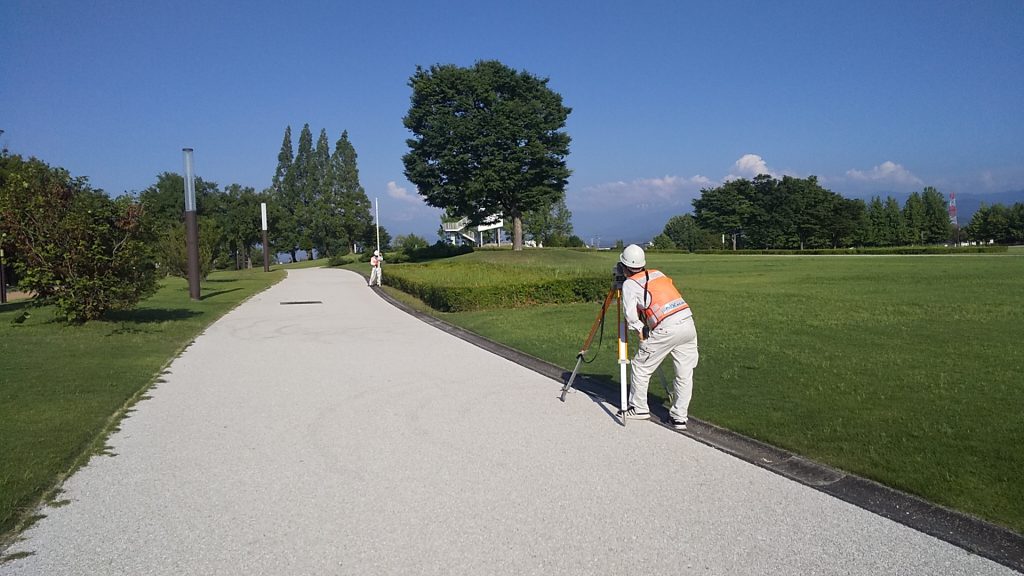

River surveying
River surveying is a type of public surveying and refers to surveys (distance marker establishment survey, bench mark, periodic longitudinal survey, periodic cross-sectional survey, and depth survey) conducted to obtain data necessary for river maintenance, management, design, and construction.
This includes surveying not only rivers but also lakes, marshes, and coasts.
During these surveys, river geometry, water levels, cross sections, velocities, flow rates, and other factors are measured and drawings are prepared.
They are also used for research to prevent the occurrence of disasters such as floods and storm surges.
Site surveying
Site surveying involves surveying land and boundaries to create the data and drawings necessary for site acquisition and other purposes. It is mainly used to clarify the land and boundaries necessary for building new roads and structures. In recent years, we have conducted remote boundary inspections to reduce the burden on landowners and improve work efficiency.
- Document research
- Reconstruction surveying
- Boundary confirmation (inspection)
- Boundary surveying
- Boundary point-to-point surveying
- Area calculation
- Final surveying in the presence of the adjacent owners
Site surveying

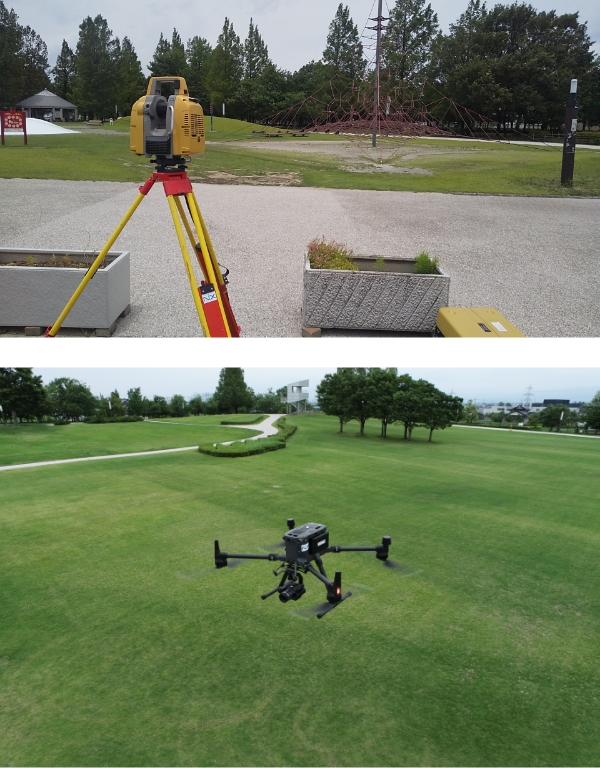
3D surveying
We are working to improve on-site productivity by utilizing ICT technology.
With various types of 3D measurement equipment, we can acquire high-precision, high-density data in a short period of time across a wide range of terrain conditions on land, at sea, and in the air.
The acquired data is converted into 3D models and provided to various fields.
Our equipment
UAVs
Terrestrial laser scanners
UAVs with laser scanners
Narrow multibeam echo-sounders
3D surveying is a method that uses equipment to measure the three-dimensional shape and position of an object or space.
Typically, optical sensors or lasers are used to acquire point cloud data from the surface of an object.
Three-dimensional surveying uses three different indices (width, depth, and height) to determine the shape of the target object.
There are several types of measurement methods, and most 3D surveying is non-contact, a method of measuring at a distance from the object of measurement (terrain or building), which has the advantage of making it easier to measure steep terrain and large structures that are difficult to access.
Below are some of the main 3D surveying methods.
Each of these methods has different characteristics and scope of application and is selected according to the objectives.
・Terrestrial laser surveying: This method uses a 3D laser scanner installed on the ground to take measurements, featuring a higher degree of accuracy than mobile surveying methods such as vehicles and drones.
・UAV photogrammetric point cloud surveying: This method uses unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to photograph terrain and buildings, extract 3D point clouds using numerical photographs, and digitally restore and measure 3D shapes.
・UAV laser surveying: This method uses drones and other UAVs to take laser measurements.
・Mobile mapping system (MMS): This method uses a vehicle equipped with a laser scanner and a 360-degree all-surrounding camera.
・Underwater sonic measurement - narrow multi-beam (NMB): This method provides real and accurate measurement of underwater topography.
3D surveying

Cadastral survey
A cadastral survey is mainly led by the municipality to investigate the owner, parcel number, and land category of each parcel of land and to survey the location and area of the boundaries. A “cadastre” is, so to speak, a “family register of land.” Just as each individual has a unique “family register” that is used in various administrative situations, “cadastral” information on land is also used in various administrative situations. When a cadastral survey is conducted, the results are sent to the registry office, where the entries in the registry are corrected and the maps are updated. The results are also used as basic information for various administrative tasks in the municipality, such as the calculation of property taxes.
- Cadastral survey Process A to Process H
- Basic survey of urban area public–private boundary
- Basic survey of mountain village boundary
- Basic survey of urban revitalization areas
Cadastral survey
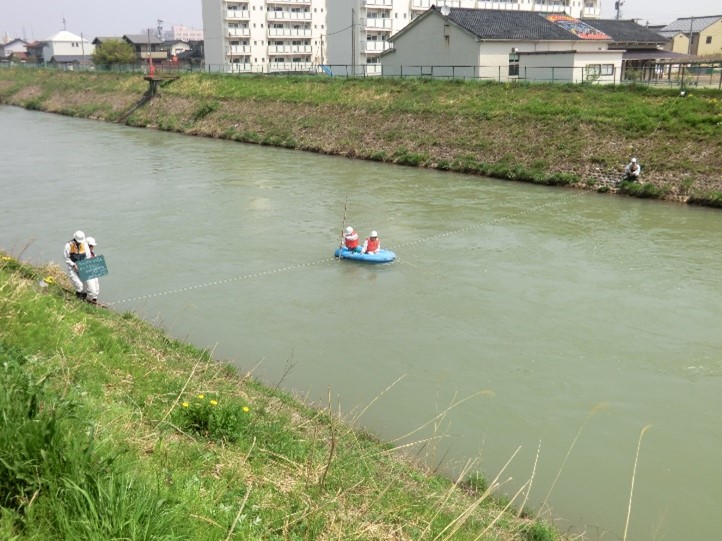
Flow rate observation
Flow rate observation refers to surveying to measure the amount of water flowing down a certain cross-section of a river in a unit of time (i.e., the river's flow rate). Flow rate observation is essential for flood control to protect the community from disasters such as floods and for “water utilization” to make use of water for daily life. We set up water level and flow rate observation stations and conduct periodic flow rate observations. An equation relating water level to flow rate is developed, and the results of daily water level observations are applied to the equation to estimate the flow rate and provide the basic data necessary for management. Normally, a current meter is used for observation, but a float is used during high water observation such as flooding.
- Low water flow rate observation
- High water flow rate observation
- Creation of water level and flow rate curves
Flow rate observation

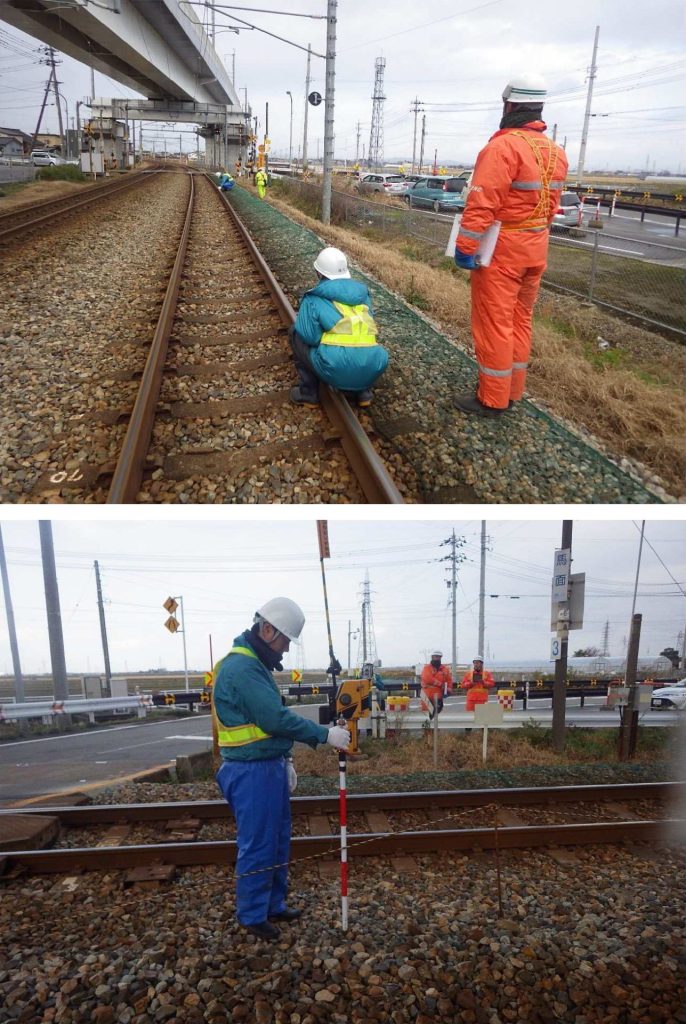
Railroad facility surveying
Railroad facility surveying refers to the measurement of the location; shape; and area of land, buildings, railway track structures, civil engineering structures, and other facilities necessary for railroad operations, collectively referred to as “railroad facilities.” Further, surveying railroad facilities is essential for the safe operation and efficient management of railroads, and we perform this work under the supervision of a qualified JR construction manager.
- Control point surveying
- Field surveying
- Centerline surveying
- Longitudinal survey
- Cross-sectional surveying
- Site surveying
Railroad facility surveying

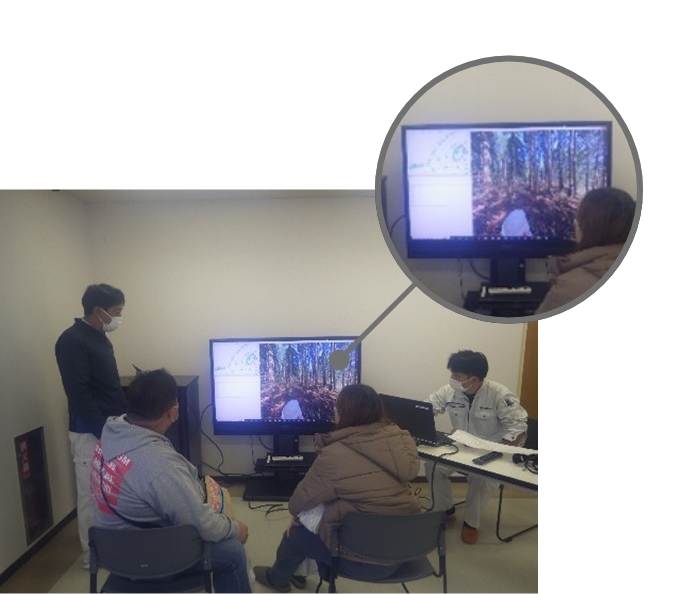
Inspection and survey DX
Using a variety of sensing technologies, we acquire 3D data as the basis for DX.
Inspection and survey DX

Forest DX
We implement forest resource surveys using BLS-type sensing technology and ICT tree analysis technology.
- Forest resource LiDAR/SLAM surveys (Forest resource survey measurements using the forest walking “BLS” method to improve survey time efficiency and acquire point cloud data.)
- Forest management ICT services (ICT for tree analysis to analyze and make high-level utilization of forest management information)
Forest DX


